Renal Replacement Therapy
Kidneys are two rajma shaped structures located on either side of the body. Each kidney contains around 10 lakh filters which clean around 1500 litres of blood per day to produce around 2 liters of urine daily. Apart from cleaning function, the kidneys do a lot more work.
- Maintenance of water quantity in the body.
- Maintaining acid-base balance in the body
- Maintaining BP in normal range
- Helping in production of blood
- Activating vitamin D and thus, maintaining bone health
Once kidney starts failing, they tend to loose all of the above functions.
The major reasons of kidney failure (chronic kidney disease) are
- Diabetes milletus
- High, uncontrolled BP
- Neglected kidney stones
- Indiscriminate use of pain killers
- Desi drugs containing heavy metals
The exact prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in India is largely unknown in absence of government CKD registry. The Indian Society of Nephrology started CKD registry in 2005 and its first report revealed average age of CKD patient as 50.1 + 14.6 years, 70% being males. In India, 48% of cases present at stage V. Diabetic Nephropathy is predominant cause of CKD (31.3%); and this number is expected to rise, as India has gained the dubious distinction of Diabetes capital of the world.
Chronic kidney disease is classified in to 5 stages, depending upon the amount of functional level left in the kidney. Untreated, the disease gradually progresses, at varying rate and may ultimately prove fatal. The major symptoms or renal failure are –
- Headache
- Loss of vitality
- Body swelling
- Aversion to food
- Nausea and vomiting
The patient may remain entirely asymptomatic in earlier stages and the disease may even spring a surprise for the patient and his family.
The treatment for the CKD is stage dependent
| Stage 1 | Healthy life style |
| Stage 2 - 4 | Medical and palliative measures. The patient requires counseling for management options of end stage disease and start preparation for the same |
| Stage 5 (End Stage) | The patient requires some form of renal replacement therapy |
Renal replacement therapy is the name given to supportive treatment in patients with CKD – stage V or End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD). Once the kidney is damaged permanently and loses all of its functions, this needs to be supported to maintain life. There are three types of RRTs
- Hemodialysis
- Peritoneal Dialysis
- Renal Transplant
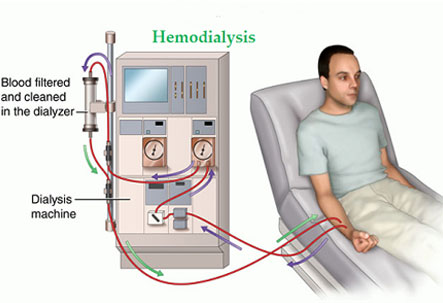
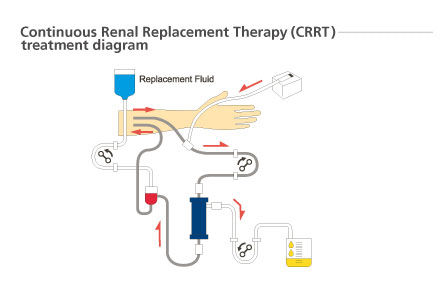
HEMODIALYSIS:
The patient’s blood is cleansed of all waste and toxic material using a hemodialysis machine. The patient needs to be hooked to dialysis machine and tubes carry patient’s blood into the machine and clean blood is again shifted back into patient. The patient needs to undergo regular dialysis sessions, ranging from 1 – 3 sessions per week depending upon condition of diseased kidneys and is decided by the nephrologist. Apart from cleaning blood, other functions of the kidney need to be taken care of with regular medications.
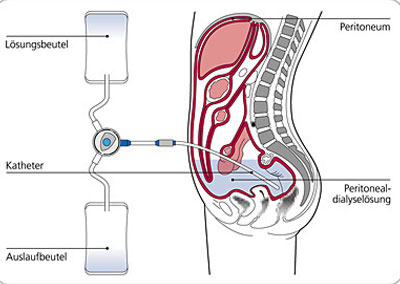
PERITONEAL DIALYSIS:
Inside the abdomen (tummy) of the patient is a thin lining through which exchange of waste material can be done. A soft silicon tube is implanted in the tummy of the patient with one end lying outside and is capped. Through this tube, dialysis fluid is instilled into the tummy, where it remains for 4-6 hours and is removed. The removal and reinstallation of fluid takes 20-30 minutes (exchange) and 3-4 exchanges are required per day. The exchange is to be done scrupulously to avoid infection. The main advantage of CAPD is independence of patient from any machine and scheduled visits to dialysis center.
Disadvantages of Hemodialysis and CAPD:
In CAPD, the patient has freedom from regular attendance to dialysis centre. But this requires high degree of cleanliness as this carries a high risk of infection.
One of the biggest adjustments to be made while taking Hemodialysis treatment is following a strict schedule. Most patients have to go to specialized dialysis center-three times a week for minimum of 3 to 5 hours per visit. A working person may face loss of job due to rigorous dialysis schedule.
Apart from this, there is always a risk of getting infected with deadly infections like Hepatitis B/C or HIV, in spite of high degree of precautions followed at modern dialysis centers. Also, even with adequate maintenance dialysis, i.e. thrice a week sessions of 4 hour each, a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of 6 – 10 ml/min only against a normal GFR or more than 90 ml/min. And even with adequate dialysis, a 5 year life expectancy is less than 50% even in best centers.
Above all these, the patient requires regular medications for maintenance of adequate hemoglobin, vitamin D and calcium homeostasis.

RENAL TRANSPLANTATION
 This is considered to be the best form of renal replacement therapy, in which a healthy kidney from the donor is transplanted into the body of the recipient. The transplanted kidney carries out all the necessary renal functions. Although the patient needs to take immunosuppressant drugs and follow certain precautions for life, he/she can return to normal life.
This is considered to be the best form of renal replacement therapy, in which a healthy kidney from the donor is transplanted into the body of the recipient. The transplanted kidney carries out all the necessary renal functions. Although the patient needs to take immunosuppressant drugs and follow certain precautions for life, he/she can return to normal life.
The donor kidney is harvested by open or laparoscopic surgery from a matched donor and placed in right lower half of recipient’s abdomen. Native kidneys are usually not touched. The graft kidney vessels are attached to the recipient vessels and ureter is attached to urinary bladder of the patient. Usually the kidney starts functioning immediately. The patient is then shifted to kidney transplant unit, and is actively monitored by the Kidney Transplant Team. The immediate post-operative period demands highly trained nursing staff with regular inputs of transplant surgeon and nephrologists. Once the patient is stabilized, he/she is down-shifted and eventually discharged. The patient has to maintain an accurate schedule to take medications as prescribed and follow a routine and healthy life-style. If properly taken care of, the graft kidney will function for years together, allowing the patient to lead a normal life style and able to contribute economically and socially to the community.
Status of treatment of CKD in India
About 74% of patients report to nephrologists, but only after the disease has progressed to CKD stage 4. Patients with higher education and better income groups tend to report early to the Nephrologist. However, almost 62% of stage 5 CKD patients are not getting any form of renal replacement therapy. Those who are getting it, 18% are going for hemodialysis, 2.5% for peritoneal dialysis and only 2% for renal transplant! The real paradox is that the best form of therapy is availed by the least number of patients.
In contrast to developed world, renal transplant (RT) rate in India is only 10 ppm per year (approx. 5000 transplants annually), of which less than 5% are from cadaveric donors.
In developed countries like USA, the figures are much higher, upto 18,000 kidney transplants annually, of which two-thirds are from cadaveric donors, rest from live donors.
The renal transplant program is in a state of transition in India. With ever increasing awareness, the rate of RT is constantly increasing. The government is also promoting deceased donor program and developing programs, wherein patients are kept on waiting list on an online registry, so that transparency is maintained. This has been most successful in the state of Tamil Nadu, and is being replicated in many other states of India.
WHO IS A CANDIDATE FOR TRANSPLANTATION?
- Life expectancy of more than 5 years
- No untreated current infection
- No recent/metastatic cancer
- No severe irreversible metastatic disease
- No psychiatric illness compromising ability to make an autonomous decision
- No drug/substance abuse abuse
- Native kidney disease with high potential to recur in transplanted kidney
WHO CAN DONATE A KIDNEY (LIVE DONOR)?
Live kidney donation is done is entirely voluntary and done out of affection and pure altruistic motive with no financial or other transection between the donor and the recipient. To be able to donate a kidney, the donor must fulfill strict medical criteria to ensure no harm is done to donor.
WHO CAN DONATE KIDNEYS?
- Age between 18 and 65 years
- Mentally fit to understand and give consent
- No H/O alcohol/drug addiction
- No H/o high BP/ Diabetes
- No H/O kidney diseases
- No H/O kidney stones
- No H/O cancer, present or treated with significant risk of recurrence
- No H/O HIV, Hepatitis B, Hepatits C, etc.
- No H/O coronary/vascular disease
WHO IS A MARGINAL DONOR?
A prospective donor, not fulfilling all of above criteria can be accepted, based on overall evaluation and explained risk.
WHAT IS BLOOD GROUP RESTRICTION?
Based on blood group of patient, he/she can accept donation from certain blood groups:
| Recipient Group | Donor Blood Group |
| O | O |
| A | A, O |
| B | B, O |
| AB | AB, A, B, O, |
There is no restriction for positive or negative blood groups.
CAN TRANSPLANTATION BE DONE ACROSS BLOOD GROUP RESTRICTION?
With technological advancements and increased understanding of immune processes, systems have been devised to transplant across blood group (ABO incompatible transplantation). It is an option for patients with non-availability of group matched donors. It has a comparable long-term survival rates
Disadvantages
a. Higher cost of transplantation ( 2 – 3) times of normal transplantation)
b. Higher earlier graft loss
WHAT IS CADEVERIC DONOR PROGRAMME?
Organs from a brain dead person are retrieved after voluntary consent from next of kin of the person and transplanted to the needy patient. Organs of a dead person can give life to 8 persons. The patient has to register him/herself to zonal/state level transplant co-ordination committee. Based on seniority of patient on the list and level of matching, organ is offered to the patient. In case of mis-match or refusal of patient, the offer is made to the next patient in list.
WHAT IS REJECTION OF TRANSPLANT KIDNEY?
Our body has got a complex immune system mechanism, which differentiates self from non-self. This is of immense importance to fight off infections. Since the transplanted graft is from different body, it is recognized as non-self and immune system is activated to destroy it. Medicines, known as "immunosuppressant drugs” stop activation of immune system and destruction of graft kidney. Inspite of all drugs, upto 30% of patients suffer from rejection, which is managed by different drugs and medicines, leading to overall success rates in excess of 95% in experienced centers. Immunosuppressant are to be taken for lifetime.
WHAT IF TRANSPLANT KIDNEY IS REJECTED
In certain cases, transplant kidney is rejected and damaged. This phenomenon can happen immediately or in a delayed fashion. The patient will have to return to dialysis and can be considered for second transplantation.
Legal Aspects of Kidney Transplant
A process, which has high potential of abuse, is tightly governed by the laws of the land ‘The Transplantation of Human Organs and Tissues Rules, 2014. Any close family member, including grandfather, grandmother, father, mother, brother, sister, son, daughter, grandson, granddaughter and spouse of the patient can volunteer to donate the kidney. The patient and donor should bring all documentary evidence to prove their relationship, which should be verified by gazetted officer or elected representative of the region. The donor and recipient undergo basic tests and specialized tests to match their compatibility and genetic profile. The more accurate the match, higher the chances of success of the graft kidney. The donor is evaluated to ensure that he/she can undergo a major surgery safely and after removal of one kidney, will be able to lead rest of his/her life without any problems. Only after a comprehensive check-up, the donor and recipient are accepted for transplant surgery.
Hospital
Address: Room No: 3, Department of Urology, Uro-oncology, Robotics And Renal Transplantation, Ground Floor, Max Super Specialty Hospital – East Block, 2, Press Enclave Road, Saket, New Delhi – 110085
Contact (For Appointments) (Call Between 9am To 5pm)
+91-9540295450, +91-9717610155, +91-9871268856
Email : ruchir.uro@gmail.com,
ruchir.maheshwari@maxhealthcare.com
Other Days: By Appointment (Sunday off)
